Chacruna (Psychotria viridis)
Psychotria viridis, also known as chacruna, belongs to the Rubiaceae (Coffee Family). Best known for its shamanistic, healing use as an additive in traditional ayahuasca in the Amazon basin, P. viridis contains a high amount of psychedelic tryptamines.
Effects
P. viridis or chacruna is essentially used today to prepare ayahuasca, a psychedelic infusion. The effects can be described as a physical and mental cleansing, and at the same time a 4-hour connection with the imperceptible.
The intensity of the "trip" depends on many factors, for most users it is necessary to gain experience and therefore at the beginning the effects will be mild. Most experience something similar to a low dose of psilocybe mushrooms or a tripi. They may also suffer from stomach cramps for the first couple of hours.
Usage
Don't underestimate how awesome the experience can be and always start with a low dosage if you are not yet familiar with Ayahuasca. In most recipes 25 grams is a low dosage and 75 is a high dosage.
If you have never prepared Ayahuasca before, keep in mind that almost no one succeeds the first time. For most people the preparation of a good Ayahuasca is the result of years of testing and experimenting.
For Ayahuasca the chacruna is usually cooked in water. Depending on the method of the manufacturer the preparation lasts from one hour to one day. Sometimes B. caapi or another plant is added to the same pot, and sometimes it has its own pot. Common cooking times vary between 4 to 12 hours. Occasionally vinegar or lemon juice is added to speed up the extraction.
In any case, the resulting liquid is reduced until a small drinkable amount is left, which is then drunk on an empty stomach.
There are people who extract this plant. The extract is used as incense, which produces a psychedelic experience of about 15 minutes that contains elements of an ayahuasca experience. Above all, there is a drastic change in the interpretation of reality and a transportation of all senses to another dimension.
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs):
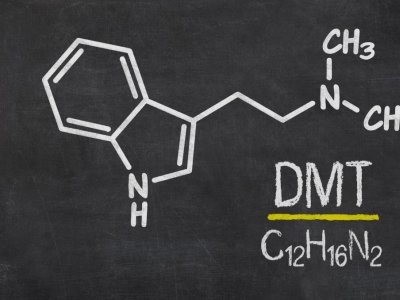
DMT(N-dimethyltryptamine) is a tryptamine alkaloid present in numerous plants such as Mimosa hostilis, Diplopterys cabrerana, Desmanthus illinoensis, Psychotria viridis and Phalaris arundinacea, is not effective when ingested orally. This is because it is broken down in the body by the enzyme monoamine oxidase (MAO). MAO is an important enzyme that destroys certain chemical compounds, such as drugs and poisons.
MAO enzyme inhibitors interfere with the action of the enzyme and stop the breakdown of chemical compounds such as DMT, making it effective when taken orally. This is the fundamental principle of the traditional visionary medicine Ayahuasca.
With the right proportions, hallucinogenic mushrooms and other psychedelic substances can be used together with MAO inhibitors. By mixing these substances with MAO inhibitors, the effect will last longer and be more intense.
MAO inhibitors should be used with great caution, otherwise normal foods can become poisonous. The results can be dangerous: headaches, nausea, loss of consciousness and death. In the shamanic tradition, MAO inhibitors are used after at least one day of fasting.
List of substances
They should not be taken at least 24 hours before and after taking an MAOI:
Prohibited Foods: avocado, caviar and substitutes, chocolate, sausages, yeasts, beans, liver, dried figs, dried and pickled fish, bananas, cheeses, coffee, beer, alcoholic beverages....
Recommended foods: Cereals, pasta, rice, eggs and legumes.
No other drugs, whether natural or synthetic, should be ingested, as many interfere with MAOIs and could have very serious consequences.
The combination of MAOIs with other substances may cause a hypertensive crisis (sudden and extreme rise in blood pressure) which may lead to the rupture of an artery in the brain, i.e. a cerebrovascular accident.